In the B2B world of advanced manufacturing (construction, agriculture, mining, and utilities), sales cycles are long, and average contract values are high (often, six figures or more). With relatively low churn, the sector still relies heavily on person-to-person sales techniques. However, technology has revolutionized the process, helping teams source more and higher quality leads while targeting those leads more efficiently before a contract is signed.
In this blog post, we will explore how technology has impacted the manufacturing sales cycle: What you should consider when adding to your automation and messaging stack, how the sector has evolved, and what’s in store for the future.

Overview
5 Sales Benefits of Marketing Technoloty
From automation to data storage to the emergence of AI, a streamlined marketing technology stack won’t just help you save money in the long run; it can help you source new leads and convert those leads more efficiently. Here are 5 ways technology can help boost your sales process.
1. You'll Work Faster
Automation technologies have simplified almost every part of the sales process. From lead generation to order processing to attribution, your team can reduce the amount of mundane, manual tasks and focus on closing.
The utilization of AI and machine learning in the analysis of sales data has proven beneficial for predicting prospects’ behaviors and market trends. Sales teams can leverage these insights to proactively address buyer’s needs and adapt their strategies accordingly.
2. Your Data is More Accurate And Accessible
Using automation tools in a CRM (customer relationship management) system helps keep your customer files clean, and easy to search. A good CRM enhances sales forecasting precision, enables accurate buyer profiling, and empowers informed decision-making.
Moreover, technology facilitates prospect segmentation based on criteria, including purchase history, preferences, and engagement levels. This segmentation approach enables effective sales strategies that significantly boost the chances of closing a deal.
3. You''ll Convert More Leads
Adopting technologies like CRMs, ERPs, and e-commerce platforms provides a view of the buyer journey. This holistic approach fosters better coordination within the sales effort leading to increased conversion rates and improved buyer retention. In addition to storing prospects, CRM systems offer insights into prospects’ interactions. Such information becomes indispensable for nurturing prospects’ relationships, understanding their evolving needs, and fostering long-term loyalty.
4. Your Data is at Your Fingertips
With the help of technology and cloud-based systems, sales teams can access real-time data. This immediate access enables responses to buyer’s inquiries, on-the-spot decision making, and the sharing of up-to-date information. These capabilities are essential.
Sales technologies offer tools that allow tracking performance indicators (KPIs) in time. This data plays a role in optimizing sales strategies, identifying effective tactics, and addressing areas that require improvement.
5. You Can Easily Scale
The fact is, new technologies allow you to do more with less. You are no longer confined by manpower or physical geography. This global reach opens up immense revenue opportunities, previously unavailable.
Evolution of Technology in Industrial Sales
Traditional Methods in Industrial Sales:
1. Face-to-Face Interactions: Traditionally, industrial sales relied heavily on in-person meetings and relationship-building.
2. Paper-Based Processes: Sales orders, invoices, and prospects records were maintained manually, leading to slower processing times and higher chances of errors.
3. Limited Data Analysis: Sales strategies were often based on limited data, gathered from personal interactions and basic record-keeping.
4. Phone and Fax Communications: These were the primary tools for outreach and follow-up.
5. Standardized Product Offerings: Customization was limited, and products were often standardized.
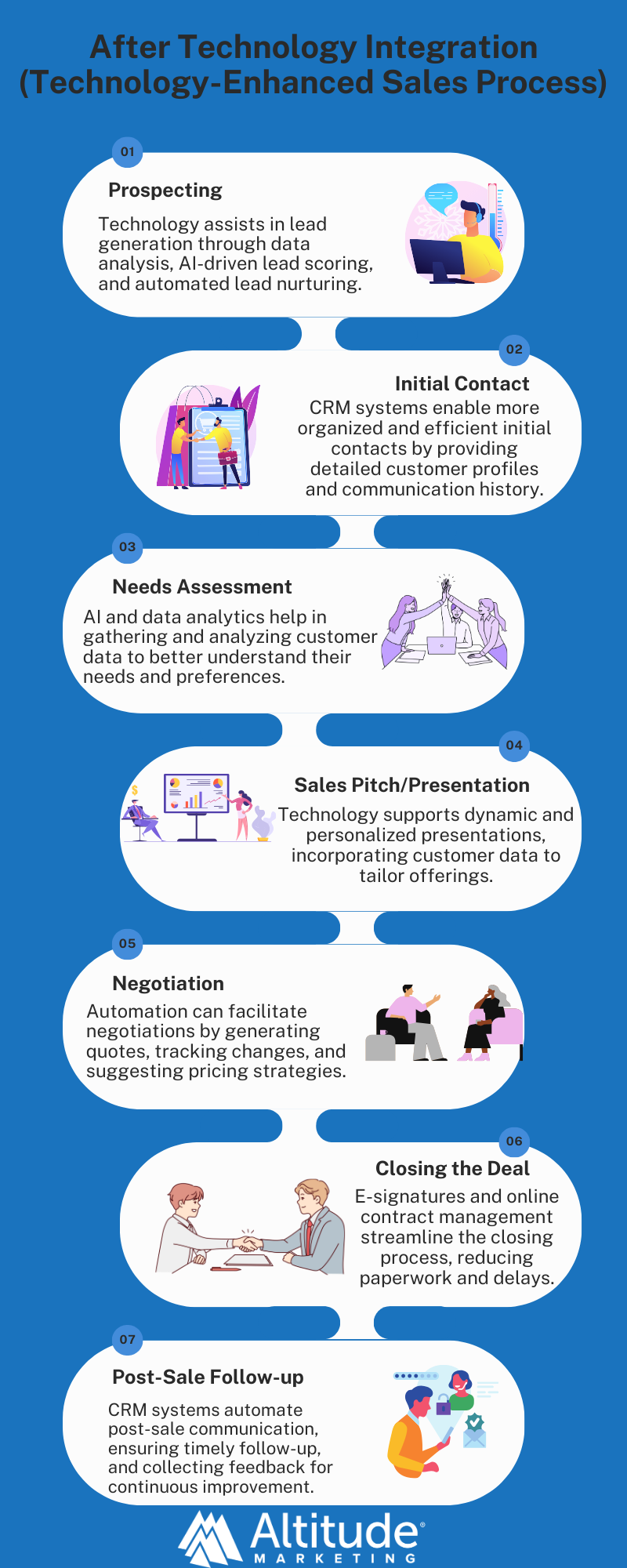
Modern Approaches in Industrial Sales:
1. Digital Communication: Email, social media, and video conferencing have supplemented (and sometimes replaced) face-to-face interactions.
2. CRM Systems: These systems centralize buyer information, streamlining sales processes and improving relationships.
3. Data-Driven Sales Strategies: Advanced analytics allow for more targeted and effective sales approaches based on comprehensive data analysis.
4. E-commerce Platforms: Online sales channels enable broader market reach and 24/7 accessibility for prospects.
5. Customization and Personalization: Technology enables more tailored products and services to meet specific buyer needs.
Here Is a quick overview of the Traditional Sales Process and Technology-Enhanced Sales Process: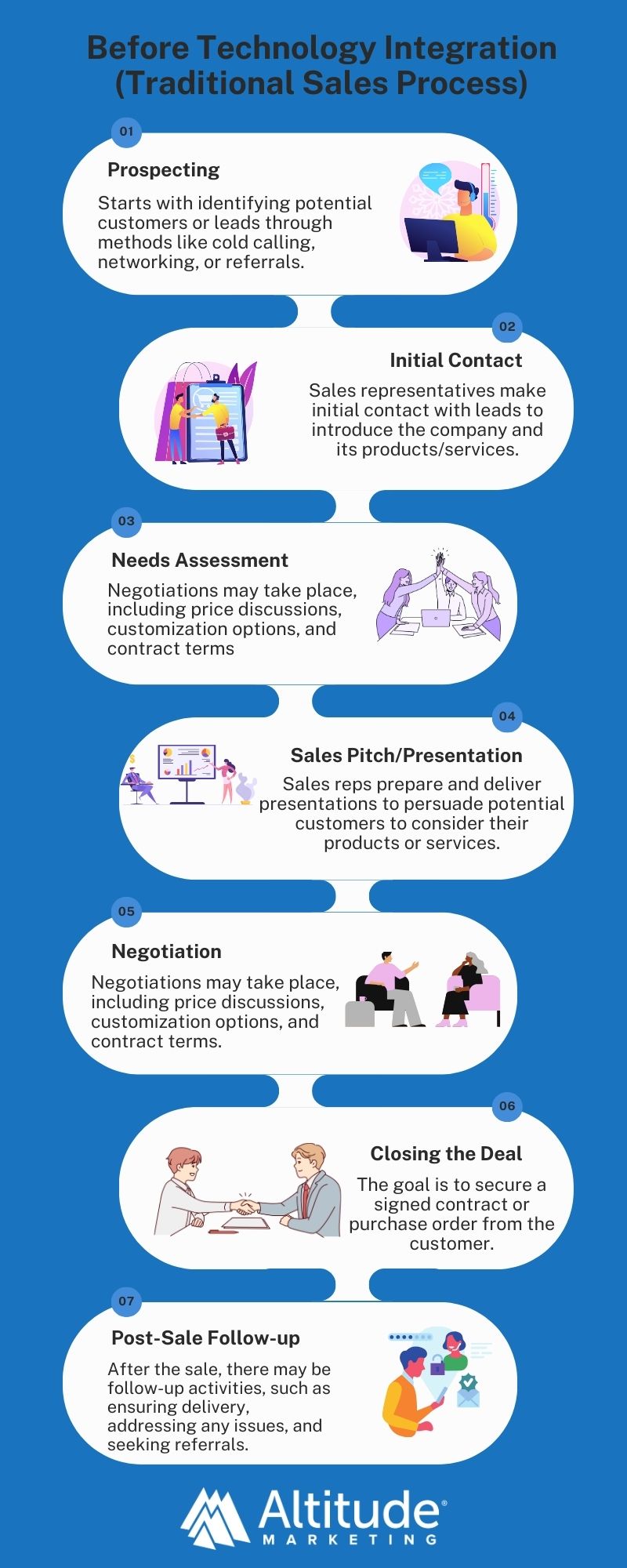
After Technology Integration (Technology-Enhanced Sales Process)
Key Technological Advancements and Their Timeline in Industrial Sales
1. 1980s – Emergence of CRM Systems: The concept of CRM emerged, focusing initially on database marketing.
2. 1990s – The Internet and Email: The widespread adoption of the Internet and email revolutionized communication in sales.
3. Early 2000s – Mobile Technology and E-commerce: The rise of e-commerce platforms and mobile technology provided new sales channels and greater mobility.
4. Mid-2000s – Social Media Platforms: Platforms like LinkedIn became crucial for networking and sales prospecting.
5. Late 2000s to Early 2010s – Cloud Computing: Cloud-based CRM systems like Salesforce became popular, offering more scalability and accessibility.
6. 2010s – Big Data and Analytics: The use of big data and advanced analytics tools allowed for more sophisticated market analysis and buyer’s insights.
7. Mid-2010s – AI and Machine Learning: AI began to be integrated into sales processes, offering predictive analytics and enhanced buyer interaction tools.
8. Late 2010s – IoT and Automation: The Internet of Things (IoT) and automation technologies started to play a role in streamlining sales operations and providing real-time data.
9. 2020s – Virtual and Augmented Reality: Emerging technologies like VR and AR are beginning to be explored for applications in industrial sales, such as virtual product demonstrations and training.
The evolution of technology in industrial sales reflects a shift from manual, relationship-based selling to a more efficient, data-driven, and buyer-centric approach. This progression has not only enhanced the efficiency of sales processes but also opened up new opportunities for personalization, buyer engagement, and market expansion.
6 Challenges Companies Must Overcome When Adopting New Marketing Technology
The integration of new technologies in industrial sales, while beneficial, comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding these challenges and implementing effective strategies is crucial for a successful technology transition. Now, let’s explore common obstacles companies face and propose strategies to overcome them.
1. Resistance to Change:
One of the primary challenges is resistance to change, especially from employees accustomed to traditional methods. This resistance can stem from fear of the unknown, lack of understanding, or perceived threats to job security.
Implementing change management strategies can help ease the transition to new technologies. This includes clear communication about the benefits, addressing employee concerns, and involving them in the transition process.
2. Training and Skill Development:
Introducing new technologies often requires new skills. Employees may lack the necessary technical expertise, leading to a skills gap.
Providing thorough training and ongoing support can bridge the skills gap. This could include workshops, online courses, and hiring or consulting with technology experts.
3. Integration with Existing Systems:
Ensuring new technologies integrate seamlessly with existing systems can be complex. Incompatibilities can lead to disruptions in business processes.
Gradually integrating new technologies can reduce disruption. Starting with pilot programs or implementing them in phases allows for adjustments based on feedback and performance.
4. Data Security and Privacy Concerns:
With the increasing reliance on digital tools, concerns about data security and privacy become more pronounced. Safeguarding sensitive information is a significant challenge.
Adopting robust cybersecurity measures and educating employees about data security best practices are essential. Compliance with data protection regulations should also be a priority.
5. Cost Implications:
The cost of acquiring, implementing, and maintaining new technologies can be substantial. Budget constraints can hinder the adoption of beneficial technologies.
Conducting a detailed cost-benefit analysis can help in understanding the financial implications and planning the budget accordingly. Exploring different financing options, such as leasing or subscription models, can be beneficial.
6. Measuring ROI:
Determining the return on investment (ROI) for new technology can be challenging, especially if the benefits are not immediately quantifiable.
Establishing clear metrics and KPIs to measure the impact of new technologies can help in assessing ROI. Regular reviews and adjustments based on these metrics can ensure continuous improvement.
5 Emerging Marketing Technology Trends in Manufacturing
The future of industrial sales is poised to be significantly influenced by emerging technologies. Innovations such as Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and the Internet of Things (IoT) are not just futuristic concepts but are gradually becoming integral to sales strategies. Let us explore these technologies and their potential impact on the future of industrial sales.
1. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
VR has already started to revolutionize product demonstrations and training in industrial sales. The industry is growing at a fast pace, with the global VR market size projected to increase from less than 12 billion U.S. dollars in 2022 to more than 22 billion U.S. dollars by 2025. Instead of relying on physical prototypes or extensive travel for in-person demos, sales teams can use VR to provide immersive and interactive product experiences remotely.
AR can enhance the buyer’s experience by overlaying digital information onto the physical world. In industrial sales, this could mean visualizing machinery or equipment in the buyer’s facility before purchase, aiding in decision-making.

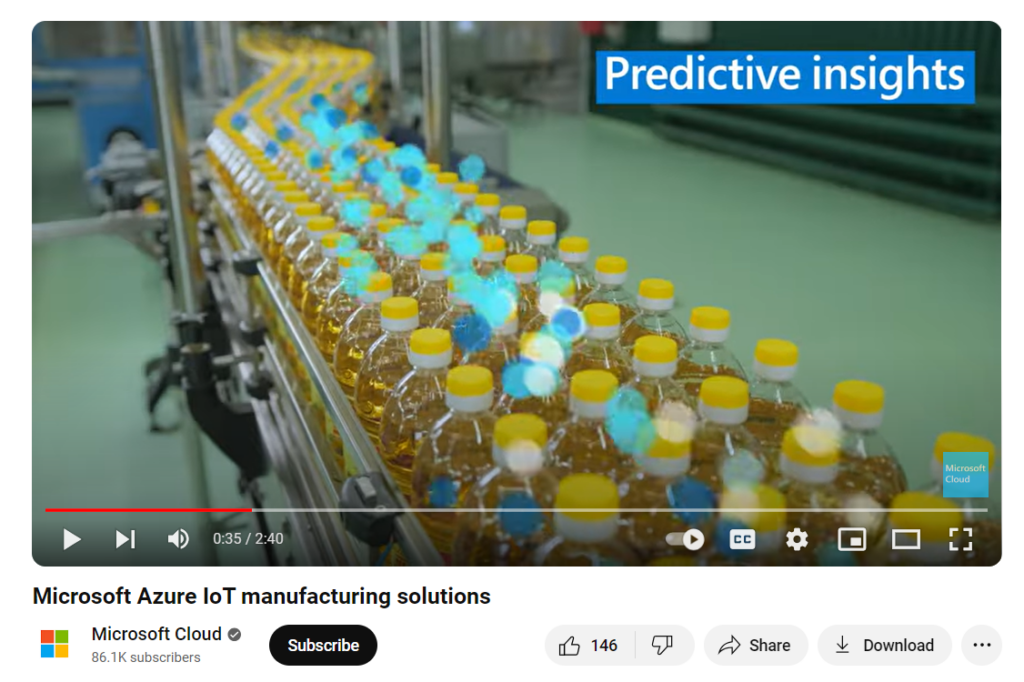
2. Industrial Internet of Things (IoT):
Industrial IoT technology is anticipated to play a more significant role in predictive maintenance, supply chain management, and buyer service. By providing real-time data from connected devices, sales teams can offer timely solutions and maintenance services, leading to better buyer relationships and upselling opportunities. They can notify clients about maintenance needs before problems arise. Having this preventative insight builds trusted advisor relationships. IoT data also informs new product offerings and upsell opportunities based on how clients use the equipment.
For example- The Microsoft Azure Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) can offer important information about how products are used, how well they perform, and what prospects prefer. This data is valuable for sales and marketing teams as it helps them understand buyer’s needs and preferences more effectively. This understanding, in turn, leads to the creation of targeted and impactful campaigns.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning:
Advanced AI is likely to become more sophisticated in analyzing prospect’s data, predicting trends, and automating more complex sales tasks. Machine learning algorithms could offer deeper insights into buyer behavior, enabling highly personalized sales approaches.
AI analyzes massive amounts of buyer data to detect subtle patterns. This provides a deep understanding of each buyer’s needs and behaviors. Sales teams can then craft tailored pitches addressing specific pain points. As AI gets more advanced, it can take over administrative tasks to free up human salespeople. AI may even engage directly with prospects via chatbots for quick inquiries. For example- using artificial intelligence to control a robotic arm that provides a more efficient way to pack boxes, saving businesses time and money.

4. Blockchain Technology:
While primarily known for its applications in finance, blockchain could offer new ways to handle transactions and contracts in industrial sales, ensuring transparency, security, and efficiency. Blockchain’s secure record-keeping could improve industrial sales contracts. It provides a transparent, unchangeable record of agreements. This builds trust between buyers and sellers. Payments can be automated when contract terms are met. Blockchain also streamlines supply chain tracing and logistics. This efficiency and security benefits sales processes.
5. 5G Connectivity:
The rollout of 5G networks will enhance the capabilities of mobile sales tools, allowing for faster data transfer, improved communication, and more robust mobile sales applications. Ultra-fast 5G networks will make salespeople constantly connected. They can instantly video conference with remote clients and colleagues. Augmented reality demos have no lag time. Smooth access to buyer data and sales tools from any location aids responsiveness and mobility. Reliable high-speed connections virtually anywhere help sales teams be more flexible and productive.
|
Technology |
Suitable Employee Size |
Suitable Business Types |
|
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) |
100-5,000 employees |
Manufacturing, Construction, Healthcare, Retail |
|
Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) |
500-10,000 employees |
Manufacturing, Transportation, Utilities, Oil/Gas |
|
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning |
1,000-50,000+ employees |
Financial Services, Marketing/Advertising, Technology, Healthcare |
|
Blockchain Technology |
1,000-50,000+ employees |
Financial Services, Supply Chain, Healthcare, Technology |
|
5G Connectivity |
1,000-50,000+ employees |
Technology, Transportation, Manufacturing, Telecommunications |
Factors to Consider When Selecting Technology for Industrial Sales
Selecting the right technology for industrial sales is a critical decision that can significantly impact a company’s success. Here, we’ll explore the key factors to consider when choosing technology solutions and the decision-making variables that businesses should weigh in their selection process.
1. Cost: Look at the upfront and ongoing money needed for the new technology. Calculate license fees, hardware, training, and maintenance. This ensures it fits the budget. Review how it can boost sales, streamline work, cut costs, and increase revenue.
2. Integration: It must work well with current systems. The technology should seamlessly connect with other sales tools used by the company. This makes sure data is consistent and workflow is smooth. Consider if the sales team will enjoy using it. Easy-to-use solutions are more likely to be accepted and succeed.
3. Scalability: The technology should grow with the business. As sales expand, it should handle more data, users and abilities without big disruptions or overhauls. Review the level of support and maintenance required. Good service and maintenance plans are key to solving issues and keeping them updated.
4. Security: For industrial sales, data security is very important. Review the protections offered, including encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry rules. Check that it matches the company’s long-term goals and industry trends. Confirm it will remain useful and supported in the coming years.
5. Customization: Being able to customize it for specific business needs is valuable. Customization means it matches the unique industrial sales processes and requirements. Consider if it will give the company an edge over competitors. Will it allow unique selling points or better buyer experiences?
6. User-Friendliness: Ease of use is critical for staff to adopt it. Simple interfaces and user-friendly features raise the chances of success and minimize the learning curve. Review its ability to provide helpful data insights and analytics. Useful data can inform smart decisions and improve sales strategies.
7. Support and Training: Having training resources and support available is key. Proper training ensures users can fully use its capabilities. Responsive support helps fix any issues quickly. Confirm it complies with industry rules and standards. Data privacy and security are extremely important to avoid legal issues and reputation damage.
8. Vendor Reputation: Research the reputation and history of the technology vendor. Reliable vendors with quality products and services are more likely to provide long-term support and updates. Check that it can easily adapt to changing business needs and market conditions. Flexible solutions can accommodate shifts in strategy and circumstances.
Ethical Considerations and Compliance in Technology-Driven Sales
1. Data Privacy and Consent: Companies need to respect buyer’s privacy and get permission when collecting data. It raises ethical worries if personal information is used without asking or if data leaks due to poor security.
2. Transparency and Honesty: Being open and truthful is key to buyer trust. Provide clear and accurate details about products, pricing, and services. Misleading claims or hiding facts can hurt trust and reputation.
3. Buyer Data Usage: It raises ethical issues if buyer data is used for other purposes than agreed on. Or if data is shared or sold without approval. Companies should clearly explain how they use data. And ensure it meets what prospects expect.
4. Algorithmic Bias: AI programs can unintentionally continue biases in their training data. Companies need to actively work to remove bias from algorithms. This ensures fair and ethical automated decision-making.
5. Accessibility: Making sales technology usable for people with disabilities is ethical and legally required. Complying with accessibility standards like the ADA is crucial. It provides equal opportunities for all prospects.
Conclusion
Technology has changed industrial sales. While relationships remain important, data and digital tools now enable smarter strategies. Adopting new technologies has challenges but worthwhile long-term gains. With planning and change management, companies can transition smoothly. Upcoming innovations will continue advancing sales. However, by upholding ethics and compliance, technology can be used responsibly for sustainable success.


